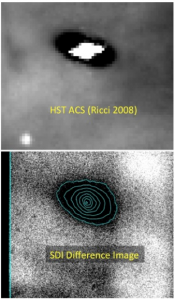
Part of Figure 1 from Follette et al. (2013), comparing the Hubble (HST) image (top) to their image (bottom) of the protoplanetary disk.
Today in journal club, we discussed two papers.
The first one was Follette+ (2013), which presented the first images of a protoplanetary disk taken using a new adaptive optics instrument on the Magellan telescope.
This disk (shown at right) is a collection of gas and dust orbiting a young star, only a few million years old. Studying these kinds of young disks help astronomers understand what the early solar system was like, when our planets were still forming.
In addition to providing new images of this disk, this paper also presented evidence that, although the disk is young, the accumulation of dust particles that gives rise to planets may already be underway. This result means that, although astronomers have thought this particular disk may show us the very earliest conditions in a protoplanetary disk, instead this disk may be fairly far along in its evolution and the process of planet formation.
The second paper we discussed was Storch & Lai (2013), which studied the origin of hot Jupiters — gas giant planets (like Jupiter) but orbiting hundreds of times closer to their host stars than the Earth does the Sun.
The origins of these planets are still unclear, but they are so close to their stars that they undergo very strong tidal interactions. These tidal interactions distort the shapes of the planets, dissipating orbital energy within the planets’ interiors and causing the orbits to shrink over time.
Determining the rates and processes of tidal dissipation are key to understanding the origins and fates of these planets: Too much tidal dissipation will overheat the planets’ interiors and blow them up; too little, and the planets wouldn’t reside in the orbits in which we see them today.
Storch & Lai (2013) include the effects of dissipation within the planets’ icy and rocky cores, which they show can help explain the origins of the planets.